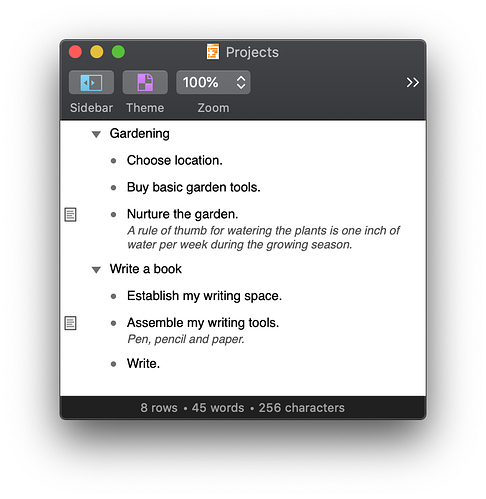
This Drafts 5 action imports a TaskPaper-formatted Draft into OmniOutliner using the new OmniJS API.
For example, starting with this text:
Gardening:
- Choose location.
- Buy basic garden tools.
- Nurture the garden.
A rule of thumb for watering the plants is one inch of water per week during the growing season.
Write a book:
- Establish my writing space.
- Assemble my writing tools.
Pen, pencil and paper.
- Write.
Produces this OmniOutliner outline:
Link:
https://actions.getdrafts.com/a/1ar
Code:
// Twitter: @unlocked2412
// DRAFTS JS CODE --------------------------------------------------------
const draftsJSContext = () => {
// main :: IO ()
const main = () => {
return runOmniJSWithArgsFromDrafts(
'omnioutliner://localhost/omnijs-run',
omniJSContext,
options
)
};
// OMNI JS CODE ---------------------------------------
const omniJSContext = opts => {
// main :: IO ()
const main = () => {
const forest = compose(
map(
compose(
fmapTree(
x => ({
topic: x.text,
note: x.note
})
),
treeWithNotes
)
),
forestFromTaskPaperString
)(opts.content)
return Document.makeNewAndShow(
doc => ooRowsFromForest(doc.outline.rootItem)(
forest
)
)
};
// GENERIC FUNCTIONS ----------------------------------
// https://github.com/RobTrew/prelude-jxa
// JS Prelude --------------------------------------------------
// Just :: a -> Maybe a
const Just = x => ({
type: 'Maybe',
Nothing: false,
Just: x
});
// Node :: a -> [Tree a] -> Tree a
const Node = v =>
// Constructor for a Tree node which connects a
// value of some kind to a list of zero or
// more child trees.
xs => ({
type: 'Node',
root: v,
nest: xs || []
});
// Nothing :: Maybe a
const Nothing = () => ({
type: 'Maybe',
Nothing: true,
});
// Tuple (,) :: a -> b -> (a, b)
const Tuple = a =>
b => ({
type: 'Tuple',
'0': a,
'1': b,
length: 2
});
// compose (<<<) :: (b -> c) -> (a -> b) -> a -> c
const compose = (...fs) =>
// A function defined by the right-to-left
// composition of all the functions in fs.
fs.reduce(
(f, g) => x => f(g(x)),
x => x
);
// div :: Int -> Int -> Int
const div = x =>
y => Math.floor(x / y);
// eq (==) :: Eq a => a -> a -> Bool
const eq = a =>
// True when a and b are equivalent in the terms
// defined below for their shared data type.
b => {
const t = typeof a;
return t !== typeof b ? (
false
) : 'object' !== t ? (
'function' !== t ? (
a === b
) : a.toString() === b.toString()
) : (() => {
const kvs = Object.entries(a);
return kvs.length !== Object.keys(b).length ? (
false
) : kvs.every(([k, v]) => eq(v)(b[k]));
})();
};
// filter :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [a]
const filter = p =>
// The elements of xs which match
// the predicate p.
xs => [...xs].filter(p);
// findIndices :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [Int]
// findIndices :: (String -> Bool) -> String -> [Int]
const findIndices = p =>
xs => (
ys => ys.flatMap((y, i) => p(y, i, ys) ? (
[i]
) : [])
)([...xs])
// first :: (a -> b) -> ((a, c) -> (b, c))
const first = f =>
// A simple function lifted to one which applies
// to a tuple, transforming only its first item.
xy => Tuple(f(xy[0]))(
xy[1]
);
// flip :: (a -> b -> c) -> b -> a -> c
const flip = op =>
// The binary function op with its arguments reversed.
1 < op.length ? (
(a, b) => op(b, a)
) : (x => y => op(y)(x));
// fmapTree :: (a -> b) -> Tree a -> Tree b
const fmapTree = f => {
// A new tree. The result of a structure-preserving
// application of f to each root in the existing tree.
const go = tree => Node(f(tree.root))(
tree.nest.map(go)
);
return go;
};
// foldTree :: (a -> [b] -> b) -> Tree a -> b
const foldTree = f => {
// The catamorphism on trees. A summary
// value obtained by a depth-first fold.
const go = tree => f(tree.root)(
tree.nest.map(go)
);
return go;
};
// fst :: (a, b) -> a
const fst = tpl =>
// First member of a pair.
tpl[0];
// isSpace :: Char -> Bool
const isSpace = c =>
// True if c is a white space character.
/\s/.test(c);
// length :: [a] -> Int
const length = xs =>
// Returns Infinity over objects without finite
// length. This enables zip and zipWith to choose
// the shorter argument when one is non-finite,
// like cycle, repeat etc
'GeneratorFunction' !== xs.constructor.constructor.name ? (
xs.length
) : Infinity;
// lines :: String -> [String]
const lines = s =>
// A list of strings derived from a single
// newline-delimited string.
0 < s.length ? (
s.split(/[\r\n]/)
) : [];
// list :: StringOrArrayLike b => b -> [a]
const list = xs =>
// xs itself, if it is an Array,
// or an Array derived from xs.
Array.isArray(xs) ? (
xs
) : Array.from(xs || []);
// map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
const map = f =>
// The list obtained by applying f
// to each element of xs.
// (The image of xs under f).
xs => [...xs].map(f);
// matching :: [a] -> (a -> Int -> [a] -> Bool)
const matching = pat => {
// A sequence-matching function for findIndices etc
// findIndices(matching([2, 3]), [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])
// -> [1, 4]
const
lng = pat.length,
bln = 0 < lng,
h = bln ? pat[0] : undefined;
return x => i => src =>
bln && h == x && eq(pat)(
src.slice(i, lng + i)
);
};
// minimum :: Ord a => [a] -> a
const minimum = xs => (
// The least value of xs.
ys => 0 < ys.length ? (
ys.slice(1)
.reduce((a, y) => y < a ? y : a, ys[0])
) : undefined
)(list(xs));
// nest :: Tree a -> [a]
const nest = tree => {
// Allowing for lazy (on-demand) evaluation.
// If the nest turns out to be a function –
// rather than a list – that function is applied
// here to the root, and returns a list.
const xs = tree.nest;
return 'function' !== typeof xs ? (
xs
) : xs(root(x));
};
// Derive a function from the name of a JS infix operator
// op :: String -> (a -> a -> b)
const op = strOp =>
eval(`(a, b) => a ${strOp} b`);
// partition :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> ([a], [a])
const partition = p =>
// A tuple of two lists - those elements in
// xs which match p, and those which don't.
xs => list(xs).reduce(
(a, x) => p(x) ? (
Tuple(a[0].concat(x))(a[1])
) : Tuple(a[0])(a[1].concat(x)),
Tuple([])([])
);
// root :: Tree a -> a
const root = tree => tree.root;
// snd :: (a, b) -> b
const snd = tpl => tpl[1];
// span, applied to a predicate p and a list xs, returns a tuple of xs of
// elements that satisfy p and second element is the remainder of the list:
//
// > span (< 3) [1,2,3,4,1,2,3,4] == ([1,2],[3,4,1,2,3,4])
// > span (< 9) [1,2,3] == ([1,2,3],[])
// > span (< 0) [1,2,3] == ([],[1,2,3])
//
// span p xs is equivalent to (takeWhile p xs, dropWhile p xs)
// span :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> ([a], [a])
const span = p =>
// Longest prefix of xs consisting of elements which
// all satisfy p, tupled with the remainder of xs.
xs => {
const
ys = 'string' !== typeof xs ? (
list(xs)
) : xs,
iLast = ys.length - 1;
return splitAt(
until(
i => iLast < i || !p(ys[i])
)(i => 1 + i)(0)
)(ys);
};
// splitArrow (***) :: (a -> b) -> (c -> d) -> ((a, c) -> (b, d))
const splitArrow = f =>
// The functions f and g combined in a single function
// from a tuple (x, y) to a tuple of (f(x), g(y))
// (see bimap)
g => tpl => Tuple(f(tpl[0]))(
g(tpl[1])
);
// splitAt :: Int -> [a] -> ([a], [a])
const splitAt = n =>
xs => Tuple(xs.slice(0, n))(
xs.slice(n)
);
// splitOn :: [a] -> [a] -> [[a]]
// splitOn :: String -> String -> [String]
const splitOn = pat => src =>
/* A list of the strings delimited by
instances of a given pattern in s. */
('string' === typeof src) ? (
src.split(pat)
) : (() => {
const
lng = pat.length,
tpl = findIndices(matching(pat))(src).reduce(
(a, i) => Tuple(
fst(a).concat([src.slice(snd(a), i)])
)(lng + i),
Tuple([])(0),
);
return fst(tpl).concat([src.slice(snd(tpl))]);
})();
// take :: Int -> [a] -> [a]
// take :: Int -> String -> String
const take = n =>
// The first n elements of a list,
// string of characters, or stream.
xs => 'GeneratorFunction' !== xs
.constructor.constructor.name ? (
xs.slice(0, n)
) : [].concat.apply([], Array.from({
length: n
}, () => {
const x = xs.next();
return x.done ? [] : [x.value];
}));
// uncons :: [a] -> Maybe (a, [a])
const uncons = xs => {
// Just a tuple of the head of xs and its tail,
// Or Nothing if xs is an empty list.
const lng = length(xs);
return (0 < lng) ? (
Infinity > lng ? (
Just(Tuple(xs[0])(xs.slice(1))) // Finite list
) : (() => {
const nxt = take(1)(xs);
return 0 < nxt.length ? (
Just(Tuple(nxt[0])(xs))
) : Nothing();
})() // Lazy generator
) : Nothing();
};
// unlines :: [String] -> String
const unlines = xs =>
// A single string formed by the intercalation
// of a list of strings with the newline character.
xs.join('\n');
// until :: (a -> Bool) -> (a -> a) -> a -> a
const until = p => f => x => {
let v = x;
while (!p(v)) v = f(v);
return v;
};
// JS Trees ----------------------------------------------------
// forestFromLineIndents :: [(Int, String)] -> [Tree String]
const forestFromLineIndents = tuples => {
const go = xs =>
0 < xs.length ? (() => {
const [n, s] = Array.from(xs[0]);
// Lines indented under this line,
// tupled with all the rest.
const [firstTreeLines, rest] = Array.from(
span(x => n < x[0])(xs.slice(1))
);
// This first tree, and then the rest.
return [
Node({
body: s,
depth: n
})(go(firstTreeLines))
].concat(go(rest));
})() : [];
return go(tuples);
};
// forestFromTaskPaperString :: String -> Tree Dict
const forestFromTaskPaperString = s => {
const
tpItemType = x => x.startsWith('- ') ? ({
text: x.slice(2),
type: 'task'
}) : x.endsWith(':') ? ({
text: x.slice(0, -1),
type: 'project'
}) : {
text: x,
type: 'note'
},
tpTagDict = xs => xs.reduce((a, x) => {
const kv = x.split('(');
return Object.assign(a, {
[kv[0]]: 1 < kv.length ? (
kv[1].split(')')[0]
) : ''
})
}, {}),
tpParse = dct => {
const
pair = splitArrow(tpItemType)(tpTagDict)(
uncons(
splitOn(' @')(dct.body)
).Just
);
return Object.assign({}, dct, pair[0], {
tags: pair[1]
});
};
return compose(
map(fmapTree(tpParse)),
forestFromLineIndents,
indentLevelsFromLines,
filter(Boolean),
lines
)(s);
};
// indentLevelsFromLines :: [String] -> [(Int, String)]
const indentLevelsFromLines = xs => {
const
indentTextPairs = xs.map(compose(
first(length),
span(isSpace)
)),
indentUnit = minimum(
indentTextPairs.flatMap(pair => {
const w = fst(pair);
return 0 < w ? [w] : [];
})
);
return indentTextPairs.map(
first(flip(div)(indentUnit))
);
};
// indentedLinesFromTrees :: String -> (a -> String) ->
// [Tree a] -> [String]
const indentedLinesFromTrees = strTab => f => trees => {
const go = indent => node => [indent + f(node)]
.concat(node.nest.flatMap(go(strTab + indent)));
return trees.flatMap(go(''));
};
// treeWithNotes :: Tree Dict -> Tree Dict
const treeWithNotes = foldTree(item => subtrees => {
const [withNotes, withoutNotes] = Array.from(
partition(
child => child.root.type === 'note'
)(subtrees)
);
return Node(
Object.assign({},
item, {
note: compose(
unlines,
indentedLinesFromTrees('\t')(
compose(
x => x.text,
root
)
)
)(withNotes)
}
)
)(
withoutNotes
)
})
// OmniOutliner OmniJS -----------------------------------------
// ooRowsFromForest :: OO Item -> [Tree] -> [OO Item]
const ooRowsFromForest = parent => trees => {
const go = parent => tree => {
const
item = parent.addChild(
null,
x => Object.assign(
x, tree.root
)
);
return (
tree.nest.map(go(item)),
item
);
};
return trees.map(go(parent));
};
// MAIN -----------------------------------------
return main()
};
// runOmniJSWithArgsFromDrafts :: URL String -> Function -> [...OptionalArgs] -> a
function runOmniJSWithArgsFromDrafts(baseURL, f) {
const
strCode = encodeURIComponent(
`(${f})(${Array.from(arguments)
.slice(2).map(JSON.stringify)})`
),
strURL = `${baseURL}?script=${strCode}`;
return app.openURL(strURL)
}
return main()
};
draftsJSContext()
Used some of the wonderful generic functions from: https://github.com/RobTrew/prelude-jxa